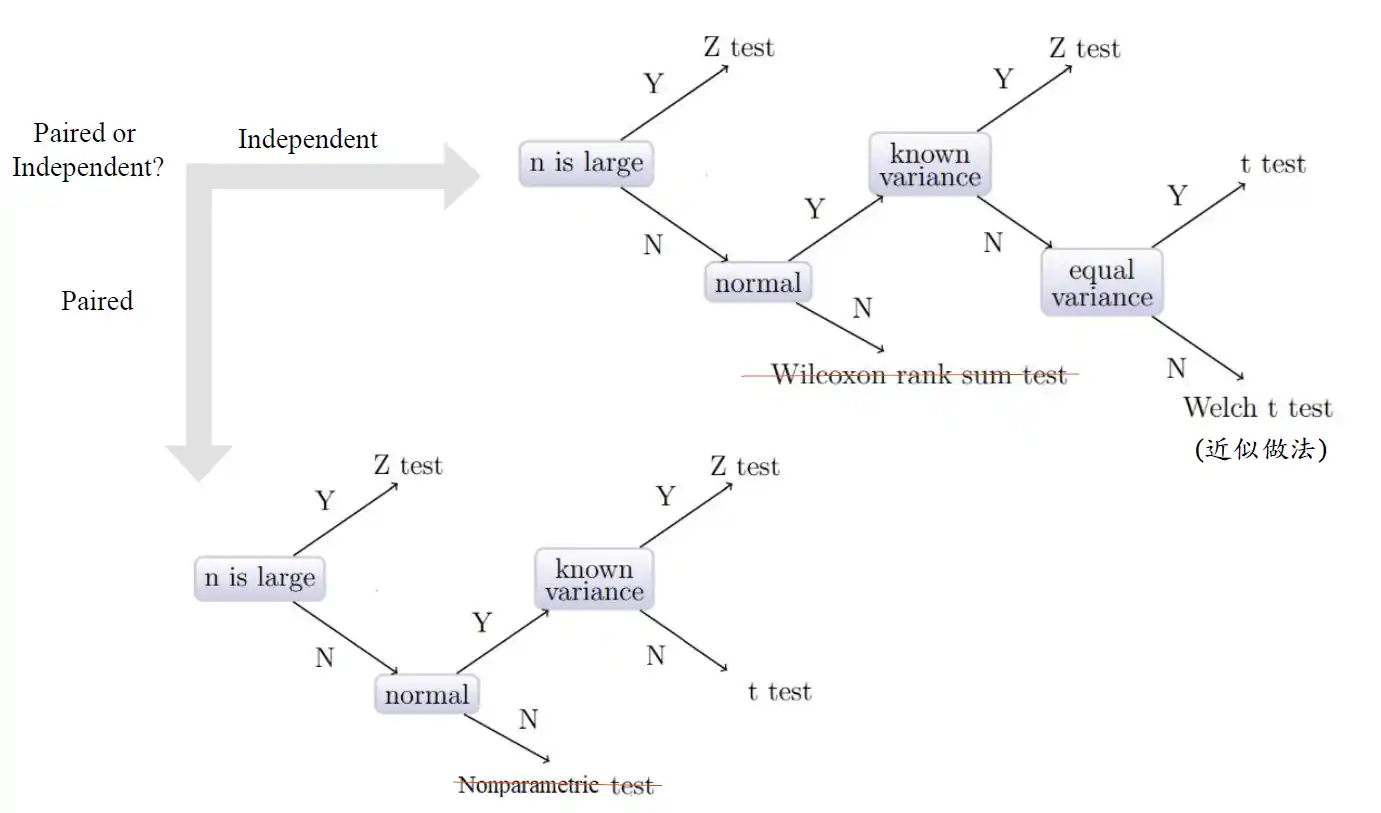
檢定兩個樣本間是否為相同母體
獨立資料和成對資料處理方式不同(變異數算法)
不變的道理
算合併標準差(pooled standard deviation)
寫出拒絕域
寫出 p 值提出拒絕 H 0 H_{0} H 0
兩獨立樣本
兩組樣本,無法一一對應。例如:
採用方法 A 和方法 B 工法的流水線產品瑕疵率
國產與進口車平均維修價格差異
X₁ and X₂ represent the annual maintenance costs of domestically produced cars and imported cars, respectively. Random samples of 10 domestically produced cars and 10 imported cars are taken, and their annual maintenance costs are recorded:
X₁ 6800 5900 6300 7800 8900 7500 6100 10500 5400 6900 X₂ 8900 9800 12350 10670 9500 8700 13400 9700 8600 8800
Assume that X₁ and X₂ are normally distributed with unknown but equal variances. At a significance level of α = 0.025, test whether the annual maintenance cost of domestically produced cars is lower than that of imported cars.
σ₁², σ₂² 已知 且σ₁²≠ σ₂²
如果有給兩樣本變異數
SE 就會變成:
σ 1 2 n 1 + σ 2 2 n 2 \sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^2}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^2}{n_{2}}} n 1 σ 1 2 + n 2 σ 2 2 σ₁², σ₂² 未知 且σ₁²= σ₂²
步驟:
寫出假設:
H 0 H_0 H 0 μ 1 ≥ μ 2 \mu_1 \geq \mu_2 μ 1 ≥ μ 2 H 0 H_0 H 0 μ 1 − μ 2 ≥ 0 \mu_1 - \mu_2\geq 0 μ 1 − μ 2 ≥ 0 H A H_A H A μ 1 < μ 2 \mu_1 < \mu_2 μ 1 < μ 2
計算兩組樣本的平均值與變異數:
x ˉ 1 = 平均維修費用 (國產) \bar{x}_1 = \text{平均維修費用 (國產)} x ˉ 1 = 平均維修費用 ( 國產 ) x ˉ 2 = 平均維修費用 (進口) \bar{x}_2 = \text{平均維修費用 (進口)} x ˉ 2 = 平均維修費用 ( 進口 ) s 1 2 , s 2 2 s^2_1, s^2_2 s 1 2 , s 2 2
合併變異數(Pooled variance):
s p o o l 2 = ( n 1 − 1 ) s 1 2 + ( n 2 − 1 ) s 2 2 n 1 + n 2 − 2 s^2_{pool} = \frac{(n_1 - 1) s^2_1 + (n_2 - 1) s^2_2}{n_1 + n_2 - 2} s p oo l 2 = n 1 � + n 2 − 2 ( n 1 − 1 ) s 1 2 + ( n 2 − 1 ) s 2 2
統計量:
n 夠大用 Z 表,太小用 t 表。這裡用 t 示範
分母就是 SE
t = x ˉ 1 − x ˉ 2 − ( μ 1 − μ 2 ) s p o o l 2 ( 1 n 1 + 1 n 2 ) t = \frac{\bar{x}_1 - \bar{x}_2-(\mu_1-\mu_2)}{\sqrt{s^2_{pool} \left(\frac{1}{n_1} + \frac{1}{n_2}\right)}} t = s p oo l 2 ( n 1 1 + n 2 1 ) x ˉ 1 − x ˉ 2 − ( μ 1 − μ 2 )
拒絕域(左尾檢定):
R : { t < t 0.025 , d f = n 1 + n 2 − 2 } R: \{ t < t_{0.025,\, df = n_1 + n_2 - 2} \} R : { t < t 0.025 , df = n 1 + n 2 − 2 }
使用 t 分布查表得臨界值,與 t 統計量比較,或計算 p 值看是否小於 α \alpha α
p -value = P ( T d f < t ) p\text{-value} = P\left(T_{df} < t\right) p -value = P ( T df < t )
做結論:若 t t t p p p H 0 H_0 H 0
σ₁², σ₂² 未知 且σ₁²≠ σ₂²(Welch's t)
無法假設變異數相同(例如兩樣本變異程度差很多),使用 Welch's t 檢定:
假設同上:
H 0 H_0 H 0 μ 1 = μ 2 \mu_1 = \mu_2 μ 1 = μ 2 H A H_A H A μ 1 ≠ μ 2 \mu_1 \ne \mu_2 μ 1 = μ 2
使用以下統計量:
t = x ˉ 1 − x ˉ 2 s 1 2 n 1 + s 2 2 n 2 t = \frac{\bar{x}_1 - \bar{x}_2}{\sqrt{\frac{s^2_1}{n_1} + \frac{s^2_2}{n_2}}} t = n 1 s 1 2 + n 2 s 2 2 x ˉ 1 − x ˉ 2
自由度用 Welch–Satterthwaite 公式近似計算:
d f = ( s 1 2 n 1 + s 2 2 n 2 ) 2 ( s 1 2 / n 1 ) 2 n 1 − 1 + ( s 2 2 / n 2 ) 2 n 2 − 1 df = \frac{\left(\frac{s^2_1}{n_1} + \frac{s^2_2}{n_2}\right)^2}{\frac{(s^2_1 / n_1)^2}{n_1 - 1} + \frac{(s^2_2 / n_2)^2}{n_2 - 1}} df = n 1 − 1 ( s 1 2 / n 1 ) 2 + n 2 − 1 ( s 2 2 / n 2 ) 2 ( n 1 s 1 2 + n 2 s 2 2 ) 2
查表找對應的 t 臨界值或計算 p 值做檢定
成對樣本(配對樣本)
兩組樣本可以一一對應,例如:
同一人服用藥物前後的血壓
同一地點兩種測量儀器量測的結果
求每對資料的差值 d i d_i d i
計算差值平均 d ˉ \bar{d} d ˉ s d s_d s d
檢定統計量:
t = d ˉ s d / n t = \frac{\bar{d}}{s_d / \sqrt{n}} t = s d / n d ˉ
拒絕域與自由度為 n − 1 n-1 n − 1
機率的情況
兩樣本原始比例相等 p₁² = p₂²
p ^ = n 1 p ^ 1 + n 2 p ^ 2 n 1 + n 2 \hat{p} = \frac{n_{1}\hat{p}_1+n_{2}\hat{p}_2}{n_{1}+n_{2}} p ^ = n 1 + n 2 n 1 p ^ 1 + n 2 p ^ 2 兩樣本原始比例不相等 p₁²≠ p₂²
步驟參考未知相同變異數 ,SE是
p 1 ( 1 − p 1 ) n 1 + p 2 ( 1 − p 2 ) n 2 \sqrt{\frac{p_{1}(1-p_{1})}{n_{1}}+\frac{p_{2}(1-p_{2})}{n_{2}}} n 1 p 1 ( 1 − p 1 ) + n 2 p 2 ( 1 − p 2 ) 只是因為機率的變異數是 p(1-p) 所以代換調原本直接用離差算出來的變異數而已